Injuries to the abdomen, like penetrating trauma or vehicular accidents often injure the bladder as well. These injuries can lead to bladder rupture in more than 95 percent of the cases, needing immediate intervention by a urologist in Karachi. Read on to know more about bladder trauma, and its consequences:
How is the bladder injured?
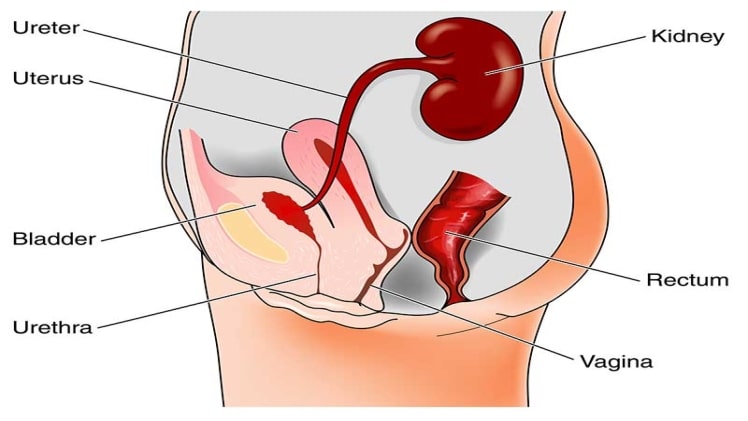
The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ that stores the urine made in the kidneys before it is excreted from the external urethra. It rests in the pelvic cavity or lower abdomen when relaxed, while filled bladder can reach the abdominal cavity.
Bladder injury can be due to penetrating trauma, iatrogenic or physician-induced trauma, or blunt injury. The extent of bladder injury depends not only on the type of trauma but also on the extent of bladder distension at the time of injury. In comparison to a relaxed bladder, a full bladder is likely to sustain a more serious injury.
Iatrogenic injuries often occur during other pelvic surgeries such as hysterectomy—removal of the uterus, or herniorrhaphy—repair of the hernia. Penetrating injuries can involve tears, bruises and cuts to the urethra and bladder. Penetrating injuries are more common in men than women.
In other cases, bladder injury can be part of straddle injury or deceleration injury during a motor vehicle collision. In such cases, the bladder is injured if it is distended and the patient is wearing a seat belt.
Previously, bladder injuries would go undiagnosed and result in high fatality. However, with timely diagnosis and appropriate management, these days, most bladder injuries have excellent outcomes. Management of bladder injuries ranges from conservative treatments to surgical repairs.
What are the symptoms of bladder injury?
Patients with bladder injury often complain of seeing blood in the urine. This is highly common with blunt injury to the bladder, in comparison to the penetrating injury which may mask the bleeding.
In addition, there is a pain in the pelvic region and just below the belly button. With concomitant injuries, bladder injuries can be hard to notice and diagnose.
In case of a bigger injury, the urine may leak into the abdomen and it is impossible to pass urine through the external urethra. If this injury involves the pelvis as well, there can be tearing of the vagina as well.
Other signs and symptoms of bladder injury include:
- Painful urination
- Pain in the abdomen
- Bloody discharge from the urethra
- Leakage of urine
- Weak urine stream
- Bloating in the abdomen
- Bruising at the site of injury
- Difficulty in initiating urination
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Pelvic pain and bruising over the genitalia
- Urine in the abdominal cavity
- Absent bowel sounds
In case of setting in of shock post-bladder injury, the patient may experience:
- Decreased alertness
- Pallor of skin
- Decreased blood pressure
- Tachycardia or high heart rate
- Skin that is cool to the touch
How is bladder injury diagnosed?
The healthcare provider begins with a thorough physical examination, that may reveal abdominal distension and tenderness. In addition, the doctor will perform a rectal exam to rule out rectal injury and evaluate the location of the prostate, which may reveal proximal urethral disruption.
The investigations to diagnose and confirm bladder injury include imaging techniques like:
X-rays: are done to evaluate pelvic bony injuries and fractures.
Computed Tomography (CT): is one of the first investigations performed in patients with abdominal trauma to check the organs and bony structures. Perforation of the bladder can be revealed through a CT scan.
Cystography: filling the bladder with contrast dye and taking x-ray scans helps to check for bladder injuries.
Surgical exploration: is another option to evaluate for bladder and other organ damage.
What are the consequences of bladder trauma?
The consequences include:
- Bleeding
- Shock
- Scarring of urethra
- Blockage of urinary flow
How is bladder injury treated?
In most cases, healthcare experts like a urologist in Lahore would perform catheter drainage until bleeding resolves. Thereafter, surgical exploration and repair may be performed, particularly for penetrating trauma and ruptured bladders.