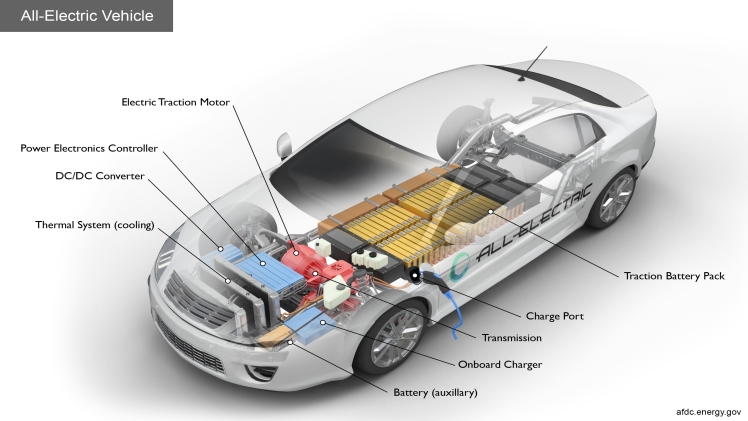
An EV is an abbreviation for an electric vehicle. EVs are cars that are partially or entirely powered by electricity. Electric cars have minimal operating expenses since there are fewer moving parts to maintain, and they are also highly ecologically friendly because they consume little or no fossil fuels (petrol or diesel).
While some EVs employed lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries are generally regarded as the norm for current battery-electric cars since they have a longer lifespan and are exceptional at storing energy, with a self-discharge rate of just 5% per month. Despite this increased efficiency, there are still issues with these batteries since they can undergo thermal runaway, which has resulted in fires or explosions in the Tesla Model S, despite attempts to enhance battery safety.
Browse professional courses after electrical engineering, designed by the industry experts to get upskilled and job-ready. Fully charging an electric car from home may cost as low as £7.80 and can even be free in public parking lots. Electric vehicles (EVs) are classified into two types: totally electric and plug-in hybrids.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
The number of moving parts in battery-powered electric cars is 99% lower than that of internal combustion engines, reducing the need for routine maintenance.
Benefits of a BEV:
- It makes very little noise
- There are no exhaust, spark plugs, clutch, or gears
- It does not require fossil fuels and instead relies on rechargeable batteries
BEVs may be charged overnight at home, providing ample range for typical travels. Long travels or those with a lot of hill climbs, on the other hand, may need to charge the fuel cells before arriving at your destination, however, regenerative braking or going downhill can assist reduce this by charging the battery packs.
An electric car’s charging time might range from 30 minutes to more than 12 hours. This is determined by the charging station’s speed and the size of the battery. In the actual world, the range is one of the most pressing issues for electric vehicles, although it is being solved by industry.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
Instead of depending exclusively on an electric motor, hybrid electric cars use a combination of battery and gasoline (or diesel) power to achieve their range. This makes them more suitable for long-distance driving since they allow you to switch to conventional fuels rather than needing to find charging stations to recharge the battery.
There are several downsides to PHEVs that are common to combustion engine cars, such as the need for greater maintenance, engine noise, and pollutants, as well as the expense of gasoline. PHEVs also have smaller battery packs, which means they have a shorter range than conventional vehicles.
An electric vehicle design course has played an important role in the development of professionals who can give expertise in terms of electric cars, assisting with the lighting of the vehicles themselves, assisting in joining and welding, preventing battery combustion, and many other aspects of the development process.